Deploy Anyscale on Kubernetes
Deploy Anyscale on Kubernetes
This page provides an overview of the permissions and resources required to deploy the Anyscale operator on Kubernetes.
You can deploy Anyscale to an existing Kubernetes cluster or deploy Anyscale alongside a new Kubernetes cluster. Supported Kubernetes clusters include Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), CoreWeave Kubernetes Service (CKS), Oracle Kubernetes Engine (OKE), or other Kubernetes clusters running in the cloud or on-prem.
Anyscale has introduced a new simplified flow for configuring an Anyscale cloud backed by Kubernetes and deploying the Anyscale operator. This flow supports GKE and EKS. See Baseline deploy for EKS and GKE.
Deploying Anyscale on other Kubernetes services requires customization for your environment. Anyscale works with customers to customize Terraform modules that deploy the operator and configure resources in your Kubernetes environment.
Contact Anyscale support for assistance customizing Terraform modules and deploying Anyscale on Kubernetes.
You can review the Anyscale Terraform modules for Kubernetes, but Anyscale doesn't recommend attempting to deploy the Anyscale operator on Kubernetes independently.
What is the Anyscale operator for Kubernetes?
The Anyscale operator for Kubernetes manages the relationship between the Anyscale control plane and your Kubernetes cluster. When you deploy Anyscale on Kubernetes, you configure a control plane role, networking, and security to allow the Anyscale control plane to use the Anyscale operator to manage resources in your Kubernetes cluster.
When you deploy the Anyscale operator on Kubernetes, Anyscale installs the operator to your Kubernetes cluster. You interact with the Anyscale control plane to configure workspaces, jobs, and services. The control plane sends instructions to the Anyscale operator to deploy Ray nodes using pods in your Kubernetes cluster.
The following diagram provides a high-level overview of the architecture of Anyscale on Kubernetes:
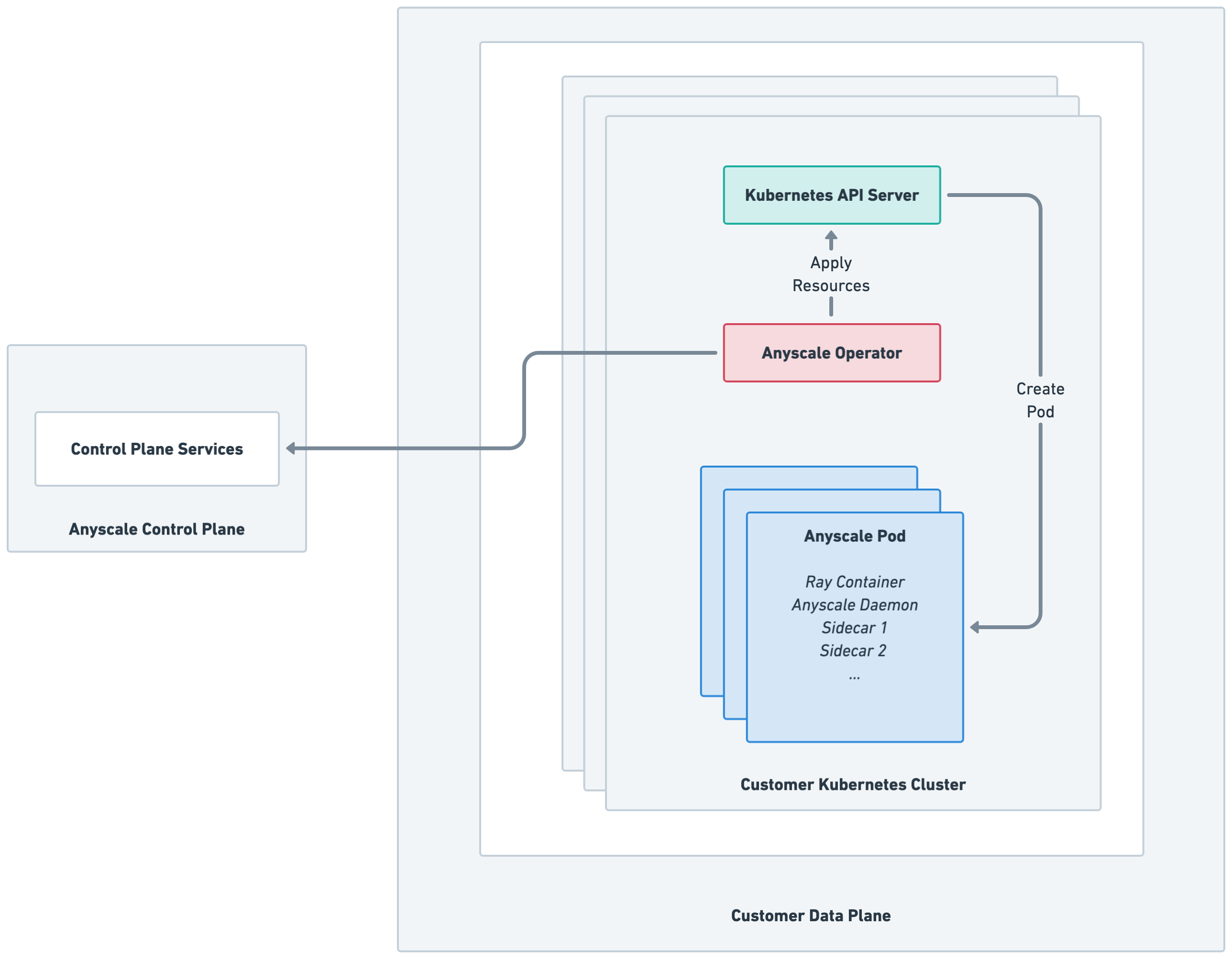
Namespace resources used by the Anyscale operator
The Anyscale operator uses the following namespace resources in your Kubernetes cluster:
- Pods: Each Anyscale node maps to a single pod.
- Services and Ingresses: Used for head node connectivity and for exposing Anyscale services. Ingresses might be either private or public.
- Secrets: Used to hold secrets used by the Anyscale operator.
- ConfigMaps: Used to store configuration options for the Anyscale operator.
- Events: Used to enhance workload observability.
Global resources used by the Anyscale operator
The Anyscale operator uses the following global resources in your Kubernetes cluster:
- TokenReview: On the startup of an Anyscale node in an Anyscale workload, Anyscale uses the Kubernetes TokenReview API to verify a pod's identity when the pod bootstraps itself to the Anyscale control plane.
- Nodes: The operator periodically reads node information to enhance workload observability.
Installing the Helm chart for the Anyscale operator requires permissions to create cluster roles and cluster role bindings, which grant the Anyscale operator the necessary permissions to manage these global resources. If you don't have these permissions, consider deploying Anyscale inside of vCluster in a Namespace of your choice.
Features missing from Anyscale on Kubernetes
Most Anyscale features have full support for Kubernetes deployments, with the following exceptions:
- Some optimization features for accelerated cluster startup aren't available.
- For zero downtime upgrades to Anyscale services, you must use an ingress controller that Anyscale can patch.
- You can't enable head node fault tolerance at the cloud level. You must configure
ray_gcs_external_storage_configin each service config and provision your own Redis-compatible cluster. See Manually configure fault tolerance for an Anyscale service.
If you don't have access to desired Anyscale features, your admin might have deployed the Anyscale operator without the required resources, networking, or permissions. Contact Anyscale support to troubleshoot your deployment.
Baseline deploy for EKS and GKE
You can use the anyscale cloud setup CLI command to configure an Anyscale cloud against an existing EKS or GKE cluster. This flow results in a working baseline configuration of Anyscale on EKS or GKE, but further configuration is necessary to unlock some features. For example, Anyscale doesn't configure shared storage during this flow.
After initial setup, you can customize your deployment by updating the Helm chart and upgrading the Anyscale operator. Some customizations might also require updates to resources in the cloud provider account, IAM permissions, or configurations for your Anyscale cloud. See Configure the Helm chart for the Anyscale operator.
The anyscale cloud setup CLI flow for Kubernetes is in beta. Anyscale recommends this flow for self-service onboarding for customers new to configuring EKS or GKE for Anyscale.
Clouds deployed and configured using this flow are production-ready and eligible for support. All features available for Anyscale on GKE or EKS are available regardless of whether you start your deployment with anyscale cloud setup or anyscale cloud register.
If you're installing the Anyscale operator to a Kubernetes environment that is highly customized, you might need to use the anyscale cloud register command and configure your Helm chart manually to install the Anyscale operator. See Deploy Anyscale to your Kubernetes cluster.
The anyscale cloud setup flow focuses on getting you to a functional baseline state quickly, then letting you customize your deployment to meet additional needs. You should plan to customize your Kubernetes environment and Anyscale cloud configurations before moving to production. You can use this flow to test your configuration in an isolated environment, then using your customized Helm chart values to install the Anyscale operator in your production Kubernetes environment.
Contact Anyscale support for assistance with configuration and customization.
Requirements
This flow installs ingress-nginx to configure ingress for the Anyscale operator in your Kubernetes cluster. Ingress is required to support features such as dashboards and Anyscale services.
If you need to use a gateway to control ingress, don't use anyscale cloud setup.
- EKS
- GKE
You must complete the following before using anyscale cloud setup to configure an Anyscale cloud on EKS:
- You must be an Anyscale organization owner.
- You must have an existing EKS cluster deployed in your AWS account.
- You must have sufficient privileges in AWS to use CloudFormation to create an S3 bucket, create IAM roles, and configure your EKS cluster.
- You must have the following CLI tools installed on your local machine:
- The Anyscale CLI
aws. See Installing or updating to the latest version of the AWS CLI.helmkubectl
- Run
anyscale loginto configure an API key for interacting with Anyscale. See Authenticate the Anyscale CLI. - Configure AWS credentials for the AWS CLI. See Configuration and credential file settings in the AWS CLI.
You must complete the following before using anyscale cloud setup to configure an Anyscale cloud on GKE:
- You must be an Anyscale organization owner.
- You must have an existing GKE cluster deployed in your Google Cloud account.
- You must have sufficient privileges in Google to create a GCS bucket, create a service account, and configure your GKE cluster.
- You must have the following CLI tools installed on your local machine:
- The Anyscale CLI
gcloudandgsutil. See Install the gcloud CLI.helmkubectl
- Run
anyscale loginto configure an API key for interacting with Anyscale. See Authenticate the Anyscale CLI. - Configure Google Cloud credentials for the Google Cloud CLI. See Authorize the gcloud CLI.
Step 1: Run the cloud setup command
- EKS
- GKE
Run the following command to begin the cloud registration flow:
anyscale cloud setup --name <cloud-name> --provider aws --stack k8s --region <region> --cluster-name <eks-name> --functional-verify
Substitute the following variables:
cloud-name: A unique name for your new Anyscale cloud.region: The AWS region containing your EKS cluster.eks-name: The name of an existing EKS cluster in the specified region for your AWS account.
Run the following command to begin the cloud registration flow:
anyscale cloud setup --name <cloud-name> --provider gcp --stack k8s --project-id <project-id> --region <region> --cluster-name <gke-name> --functional-verify
Substitute the following variables:
cloud-name: A unique name for your new Anyscale cloud.project-id: The name of the Google Cloud project containing your GKE cluster.region: The Google Cloud region containing your GKE cluster.gke-name: The name of an existing GKE cluster in the specified region for your Google Cloud account.
Step 2: Specify a namespace
The CLI prompts you to provide a namespace. Leave blank to accept the default value, or specify a new or existing namespace.
Anyscale recommends using a dedicated namespace for each Anyscale cloud registered to a Kubernetes cluster. See Namespace resources used by the Anyscale operator.
Step 3: Monitor progress
The CLI reports progress as it discovers information about your Kubernetes cluster and configures resources in your cloud provider account and Anyscale. The CLI completes the following steps:
- EKS
- GKE
- Does Kubernetes environment discovery.
- Configures and verifies
kubeconfig. - Creates a CloudFormation stack. This stack completes the following:
- Creates an S3 bucket.
- Configures an IAM role for the Anyscale operator. See Configure IAM roles for clusters on Anyscale on EKS.
- Registers an Anyscale cloud using the IAM role and S3 bucket.
- Generates a Helm chart values file with all values captured about your EKS and AWS environments.
- Installs the Anyscale operator in the specified namespace on your EKS cluster.
- This step configures and installs an
ingress-nginxpod. See the GitHub for Ingress NGINX Controller.
- This step configures and installs an
- Verifies that all configured and deployed resources communicate as expected.
- Kubernetes environment discovery.
kubeconfigconfiguration and verification.- Runs Google CLI commands to complete the following:
- Create an Google Cloud Storage (GCS) bucket.
- Configure a Google Cloud service account for the Anyscale operator. See Configure service accounts for clusters on Anyscale on GKE.
- Registers an Anyscale cloud using the service account and GCS bucket.
- Generates a Helm chart values file with all values captured about your GKE and Google Cloud environments.
- Installs the Anyscale operator in the specified namespace on your GKE cluster.
- This step configures and installs an
ingress-nginxpod. See the GitHub for Ingress NGINX Controller.
- This step configures and installs an
- Verifies that all configured and deployed resources communicate as expected.
If you encounter errors during this flow, the CLI doesn't attempt to remove any resources or configurations from successfully completed steps.
For assistance troubleshooting setup errors, contact Anyscale support and provide the CLI output.
You must have sufficient privileges in the target AWS or Google Cloud account to troubleshoot the installation. If you lack privileges, contact your cloud provider admin to request privileges or include your cloud provider admin in your Anyscale support request.
Object storage and IAM roles for Kubernetes deployments�
All Anyscale deployments on Kubernetes require access to a cloud object storage location to persist production artifacts, which include cluster logs, workspace snapshots, workload checkpoints, and cached container images. All Pods, the Anyscale operator, and the Anyscale control plane must have permissions to read and write files to this storage location.
If you use a managed Kubernetes service, you should configure the default object storage location using resources in the same account. See Requirements for Anyscale on managed Kubernetes services.
If you're deploying to a custom Kubernetes cluster such as on-prem, you can choose an object storage location in any cloud provider. See the following docs for details:
- Extend AWS IAM roles to workloads outside of AWS with IAM Roles Anywhere
- Workload Identity Federation
- Authorize access to data in Azure Storage
Requirements for Anyscale on managed Kubernetes services
You can deploy the Anyscale operator to Kubernetes services managed by AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
You must configure IAM permissions and a storage location in your cloud provider account.
| Cloud provider managed Kubernetes service | Default storage location | IAM requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) | An S3 bucket, ideally in the same region and account for simplified setup and reduced ingress and egress costs. |
|
| Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) | A Google Cloud Storage (GCS) bucket, ideally in the same region and project for simplified setup and reduced ingress and egress costs. |
See About Workload Identity Federation for GKE |
| Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) | A blob storage container, ideally in the same region and account for simplified setup and reduced ingress and egress costs. |
|
Requirements for Anyscale on other Kubernetes clusters
Anyscale supports deploying the operator to most Kubernetes clusters, including on-prem.
To get full access to Anyscale platform features, you must configure a default storage account and IAM permissions in AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud alongside your custom or on-prem Kubernetes cluster. See Object storage and IAM roles for Kubernetes deployments.
General requirements for deploying Anyscale on Kubernetes
Each Anyscale deployment to Kubernetes is a custom deployment based on how you configure and run Kubernetes.
Contact Anyscale support to get started deploying on Kubernetes.
Consider the following requirements and recommendations when choosing to deploy to Kubernetes:
- Use a Kubernetes cluster v1.28 or later when possible.
- Grant Anyscale permissions to deploy a Helm chart into the Kubernetes cluster.
- Permissions on a Kubernetes Service Account that has permissions to operate core Kubernetes resources.
- Identify the name of target Kubernetes Namespace to deploy the Anyscale operator.
- Configure the Ingress NGINX controller and set the following properties:
- allow-snippet-annotations set to
true. - annotations-risk-level set to
Critical. - enable-underscores-in-headers set to
true.
- allow-snippet-annotations set to
- Egress to the internet from Anyscale pods deployed into the Kubernetes cluster. This is a requirement of all Anyscale deployments.
- If using GPUs with EKS or AKS, configure the k8s-device-plugin.
- This isn't required to use GPUs with GKE.
- You must decide how to configure your load balancer and networking rules:
- If you choose direct networking, configure an internet-facing load balancer that opens port 443 access to the head pod.
- For custom networking, configure an internal load balancer.
- In some cases, you can apply an annotation on the LoadBalancer service in front of the NGINX pods to configure internal load balancing.
Anyscale also supports using Kubernetes Gateway and Istio as ingress controllers. Other ingress controllers might work, but Anyscale hasn't tested them and doesn't guarantee support.
Anyscale hasn't tested earlier versions of Kubernetes and doesn't guarantee support.
Deploy Anyscale to your Kubernetes cluster
Configuring and deploying Anyscale on Kubernetes requires admin privileges across Anyscale, Kubernetes, and your cloud provider account. The specifics for each deployment vary based on the requirements and existing configuration for your Kubernetes cluster. This section provides you with a high-level walkthrough of this process, which includes the following actions:
- Configure and install the Anyscale operator on your Kubernetes cluster.
- Create and configure resources and permissions in your Kubernetes cluster and cloud provider account.
- Configure the Anyscale cloud in your Anyscale organization.
If you're using EKS or GKE, consider using the simplified setup. See Baseline deploy for EKS and GKE.
You can install the Anyscale CLI on your Kubernetes cluster to run the provided commands in the same session as the helm commands.
You can optionally instead run all Anyscale CLI commands from your local terminal.
Step 1: Add the Anyscale operator Helm charts to your Kubernetes cluster
You install the Anyscale operator using a Helm chart. See the Anyscale Helm chart repository.
You must add the Anyscale operator Helm charts as a Helm repo. Anyscale regularly releases updates to the Anyscale operator through the https://anyscale.github.io/helm-charts repository. Anyscale recommends using the latest version of the Anyscale operator. For release notes and breaking changes, see the Anyscale operator releases page.
Run the following command on your Kubernetes cluster to add and cache the latest version of the Anyscale operator Helm charts:
helm repo add anyscale https://anyscale.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update anyscale
Step 2: Configure Kubernetes and cloud provider account infra
Deploying an Anyscale cloud on Kubernetes requires customization for your environment. Anyscale works with customers to customize Terraform modules that deploy resources in your cloud provider account or other Kubernetes environment.
Contact Anyscale support for assistance customizing Terraform modules and deploying Anyscale to Kubernetes.
You can review the Anyscale Terraform modules for Kubernetes, but Anyscale doesn't recommend attempting to deploy an Anyscale cloud on Kubernetes independently.
You must provide values captured from your Kubernetes cluster and cloud provider account for each of the remaining steps. Depending on how you've configured Kubernetes, you might need to set additional options not specified in these instructions.
Step 3: Configure Helm chart values
Before you install the Anyscale operator, create a custom values file (for example, my-custom-values.yaml) with configuration settings for your Kubernetes cluster.
Don't modify the Anyscale-provided values.yaml file. Instead, create your own custom values file with only the parameters you need to set. When you install or upgrade, Helm merges your custom values with Anyscale's defaults.
Your custom values file should include:
- Required configurations such as
global.cloudDeploymentId,global.cloudProvider,global.aws.region(for AWS), andglobal.auth.iamIdentity. - Optional customization such as custom instance types, networking settings, Karpenter support, or custom patches.
See Configure the Helm chart for the Anyscale operator for configuration procedures and Kubernetes Helm configuration reference for a complete parameter reference.
Step 4: Register your Anyscale cloud
You use the Anyscale CLI to register a new Anyscale cloud on Kubernetes. See CLI configuration.
The following code examples show the syntax for deploying Anyscale on EKS, GKE, AKS, and cloud agnostic Kubernetes. Adapt and run the command from the Anyscale CLI:
- EKS
- GKE
- AKS
- Cloud agnostic
anyscale cloud register --name <cloud-name> \
--provider aws \
--region <region> \
--compute-stack k8s \
--kubernetes-zones <comma-separated-zones> \
--anyscale-operator-iam-identity <anyscale-operator-iam-role-arn> \
--cloud-storage-bucket-name s3://<cloud-storage-bucket-name> \
anyscale cloud register --name <cloud-name> \
--provider gcp \
--region <region> \
--compute-stack k8s \
--kubernetes-zones <comma-separated-zones> \
--anyscale-operator-iam-identity <anyscale-operator-service-account-email> \
--cloud-storage-bucket-name gs://<cloud-storage-bucket-name>
anyscale cloud register --name <cloud-name> \
--provider azure \
--region <region> \
--compute-stack k8s \
--cloud-storage-bucket-name abfss://<container-name>@<storage-account-name>.dfs.core.windows.net \
--cloud-storage-bucket-endpoint https://<storage-account-name>.blob.core.windows.net
anyscale cloud register --name <cloud-name> \
--provider generic \
--region <region> \
--compute-stack k8s \
--cloud-storage-bucket-name <(s3://, gs://, or abfss://cloud-storage-bucket-name)> \
--cloud-storage-bucket-endpoint <(https://object.lga1.coreweave.com/ or https://<storage-account-name>.blob.core.windows.net, for example)>
Step 5: Install the Anyscale operator
The following command installs the Anyscale operator to the specified namespace in your Kubernetes cluster using the specified <release-name>.
The following examples use the --set-string option to set numerous parameters. For easier maintenance, Anyscale recommends you set these parameters in your custom values.yaml file.
The Anyscale CLI emits your cloud deployment ID when you register a cloud. Run the following command if you need to retrieve this cloud deployment ID:
anyscale cloud config get --name <cloud-name>
- EKS
- GKE
- AKS
- Cloud agnostic
helm upgrade <release-name> anyscale/anyscale-operator \
--set-string global.cloudDeploymentId=<cloud-deployment-id> \
--set-string global.cloudProvider=aws \
--set-string global.aws.region=<region> \
--set-string workloads.serviceAccount.name=anyscale-operator \
--namespace <namespace> \
--create-namespace \
-i
helm upgrade <release-name> anyscale/anyscale-operator \
--set-string global.cloudDeploymentId=<cloud-deployment-id> \
--set-string global.cloudProvider=gcp \
--set-string global.auth.iamIdentity=<anyscale-operator-service-account-email> \
--set-string workloads.serviceAccount.name=anyscale-operator \
--namespace <namespace> \
--create-namespace \
-i
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding <anyscale-operator-service-account-email> \
--role roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser \
--member "serviceAccount:<project-id>.svc.id.goog[<namespace>/anyscale-operator]"
# Generate an API key for an Anyscale service account and set it as an environment variable.
export ANYSCALE_CLI_TOKEN=<cli-token>
helm upgrade <release-name> anyscale/anyscale-operator \
--set-string global.cloudDeploymentId=<cloudDeploymentId> \
--set-string global.cloudProvider=azure \
--set-string global.auth.anyscaleCliToken=$ANYSCALE_CLI_TOKEN \
--set-string workloads.serviceAccount.name=anyscale-operator \
--namespace <namespace> \
--create-namespace \
-i
# Generate an API key for an Anyscale service account and set it as an environment variable.
export ANYSCALE_CLI_TOKEN=<cli-token>
helm upgrade <release-name> anyscale/anyscale-operator \
--set-string global.cloudDeploymentId=<cloudDeploymentId> \
--set-string global.cloudProvider=generic \
--set-string global.auth.anyscaleCliToken=$ANYSCALE_CLI_TOKEN \
--set-string workloads.serviceAccount.name=anyscale-operator \
--namespace <namespace> \
--create-namespace \
-i
Step 6: Verify your deployment
The Anyscale operator starts posting health checks to the Anyscale control plane.
To verify the Anyscale operator installed correctly, run the following command from your Anyscale CLI:
anyscale cloud verify --name <cloud-name>
Uninstall the Anyscale operator
To uninstall the Anyscale operator, run the following command on your Kubernetes cluster:
helm uninstall <release-name> -n <namespace>
kubectl delete namespace <namespace>
To delete the Anyscale cloud, run the following command from your Anyscale CLI:
anyscale cloud delete --name <cloud-name>